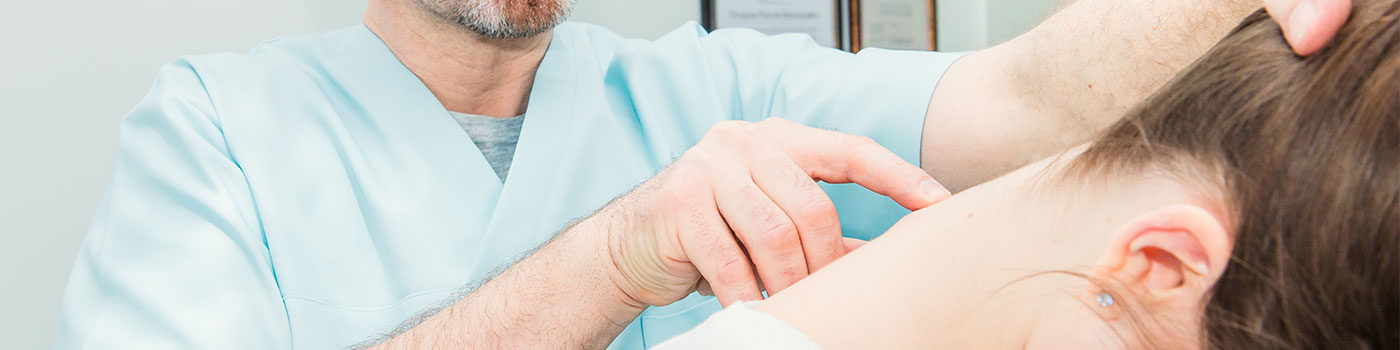
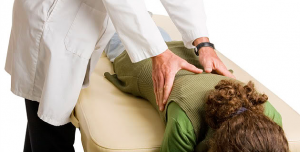
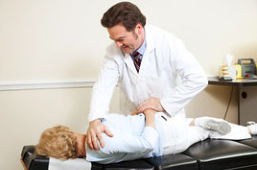
Researchers have studied spinal manipulation for a number of conditions ranging from back, neck, and shoulder pain to asthma, carpal tunnel syndrome, fibromyalgia, and headaches. Much of the research has focused on low-back pain, and has shown that spinal manipulation appears to benefit some people with this condition. A 2010 review of scientific evidence on manual therapies for a range of conditions concluded that spinal manipulation/mobilization may be helpful for several conditions in addition to back pain, including migraine and neck-related headaches, neck pain, upper- and lower-extremity joint conditions, and whiplash-associated disorders. The review also identified several conditions for which spinal manipulation/mobilization appears not to be helpful including asthma, hypertension, and menstrual pain or the evidence is inconclusive fibromyalgia, mid-back pain, premenstrual syndrome, sciatica, and temporomandibular joint disorders.